Have you ever wondered about those boxes of salt next to dishwasher detergent at the grocery store? The often-overlooked item plays a crucial role in maintaining your dishwasher’s performance and lifespan. In this guide, we delve into the significance of dishwasher salt, exploring why it’s essential, where to put it, and how to use it effectively.
Dishwashers have an internal water softener to remove calcium and magnesium from the water, making it soft. The water softener uses salt (NaCl) as the active chemical to regenerate the softener between dishes.
Want to know more about Dishwasher salt, read What is dishwasher salt?
Soft water makes the detergent more effective and will help with reducing limescale and streaks on your dishes. A visual indicator of hard water that’s not treated is that it will cause glasses to become cloudy over time.
A risk of not using soft water is blocked washer jets and deposit on the heating element and inside the machine from limescale, shortening the life of the machine.
Not all dishwasher uses salt and rely on the water coming into them to already be treated. It’s normal in some counties, like the USA, to have a home water softener unit installed on the ongoing water to the house. Therefore any appliances downstream of this will already have the water being treated.
Where do you put salt in the dishwasher?
The salt reservoir is located at the bottom of your dishwasher. After removing the lower tray unscrew the big lid covering the reservoir. Most manufacturers will include a funnel to make it easier to fill it with dishwasher salt.
What type of salt do you put in the dishwasher?
Always use salt that’s meant for use in dishwashers, like Finish Dishwasher Salt from Amazon. Even if the salt’s chemical formula is the same chemical formula we normally call table salt, sodium chloride (NaCl). Dishwasher salt is designed to dissolve gradually and not to block the softener unit, that’s why it has a coarse structure. Normal table salt might have anticoagulants that could lead to clogging of the dishwasher or the addition of magnesium salts, the chemical the softener tries to remove.
How much salt to put in the dishwasher
Different dishwashers will have differently sized units that take various amounts of salt, so there’s no precise measurement for this process.
The rule of thumb is to pour salt into the unit until it’s filled up, but not over the waterline. Since you also have water in the unit, you will be creating a saltwater brine. It is this brine that is used to regenerate the resin system inside the dishwasher.
How often do you put salt in the dishwasher?
No recommendation fits all and it will come down to the hardness of your water. Most manufacturers like Bosch has a salt indicator light to indicate when it needs a refill. A good recommendation is to check the salt level every month and just top it up. Remember that salt has a very important job and will impact the life of your dishwasher if you stop using it.
Do I need dishwasher salt in the soft water area?
Yes, even if you are living in an area with soft water you should put salt in the compartment. What you can do is adjust the water hardness setting in your dishwasher to be suitable for soft water. This will make the machine use less amount of salt brine and it will last you a long while before you need to refill.
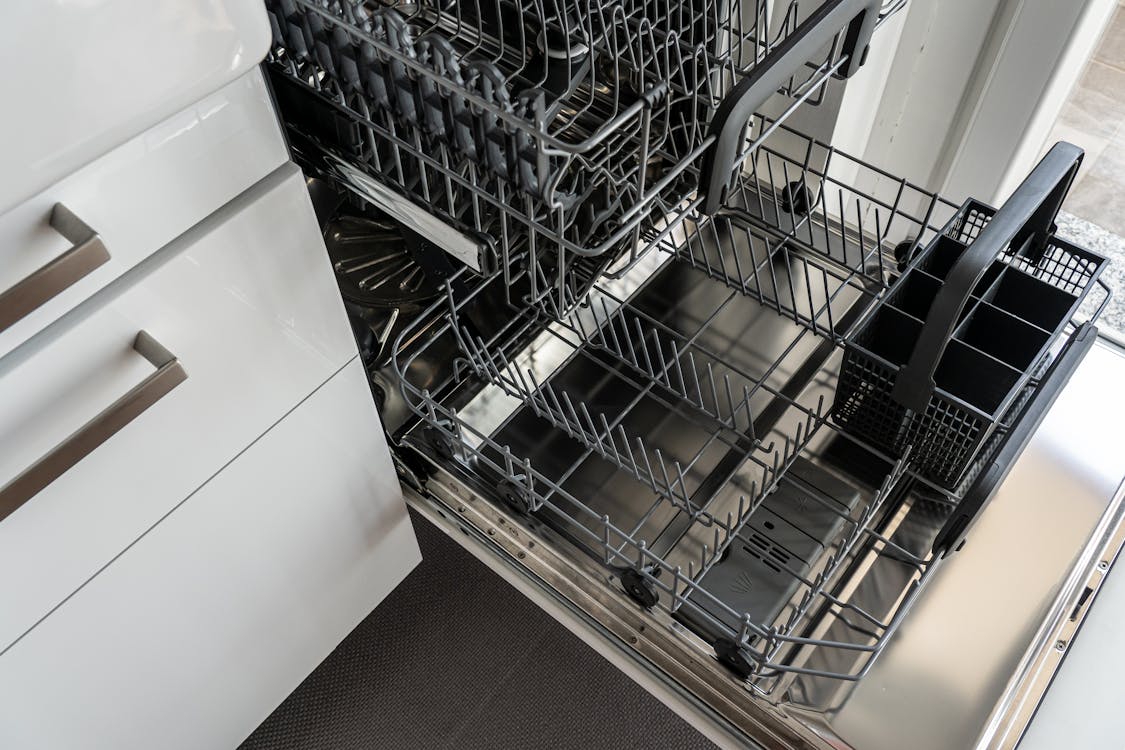

Why the dishwasher salt reservoir is full of water
When refilling the salt in the reservoir, commonly, it’s filled with water and some might even flood out. Even if it’s the first time the machines are tested in the factory.
This is absolutely nothing to be concerned about and, normally, there is water in the salt reservoir. The volume of the salt will as you pour it in displaces some of the water and it floods out as the reservoir gets filled.
The salt reservoir is part of the dishwasher’s water softening system making a salt brine, a salt solution when the salt gets mixed with the water. This requires water to be in the reservoir. The salt brine is then pulled from the reservoir to be used when regenerating the resin in the water softener inside the machine.
What does rinse aid do?
Another thing that you need to fill up in your dishwasher is the rinse aid solution. As the name suggests rinse aid will help the dishwasher to rinse off the water from your dishes.
The rinse aid works by reducing the surface tension of water, just like a normal dish soap does. Reducing the tension will make the water not stick to surfaces as easily and therefore can drain and evaporate away.
The results are that it helps to prevent watermarks on your glasses, and in combination with soft water, this will make your glassware sparkling and crystal clear.
Rinse aid also helps with the drying process enabling your dishes to dry quicker. If are you having a problem with wet dishes, check your rinse aid level.
There is no risk of running without a rinse aid like salt in a dishwasher.
How to use rinse aid
The rinse aid compartment is usually located in the door of the dishwasher next to the detergent compartment, it’s a solution you pour in.
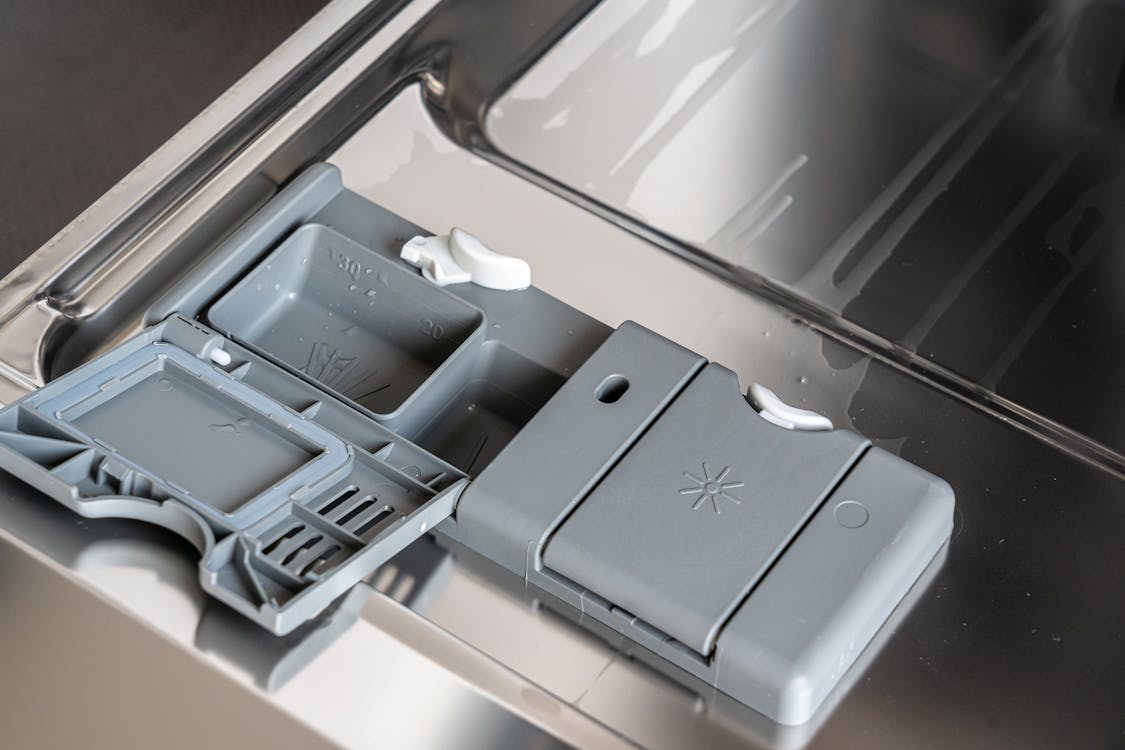

Check every couple of weeks to see if you need to fill up the rinse aid. The frequency will depend on how often you do washes.
Some dishwashers can increase the amount of rinse aid delivered for the drying process. This is often done by a small dial or leaver under the rinse aid lid. Check your machine if you are not happy with the drying result.
What is hard water?
Water hardness refers to the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in the water. If you have hard water you might notice it from a film on your drinking glasses or the reduced efficiency of soap. This can be felt when washing your hands and they still feel slimy when you are done. The easiest way is to contact your local water plant and get the amount of calcium carbonate in your drinking water.
General guidelines for classification of waters are: 0 to 60 mg/L (milligrams per liter) as calcium carbonate is classified as soft; 61 to 120 mg/L as moderately hard; 121 to 180 mg/L as hard; and more than 180 mg/L as very hard. (USGS)
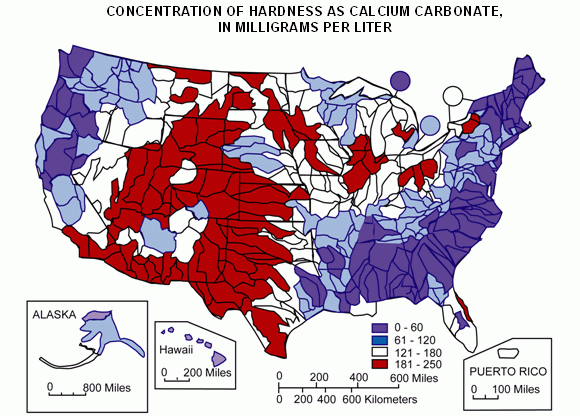
https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/cir1360
Summary:
Dishwashers, equipped with internal water softeners, rely on salt to remove calcium and magnesium from water, ensuring its softness. Soft water enhances detergent effectiveness, minimizes limescale, and prevents streaks on dishes. Neglecting dishwasher salt risks issues like blocked washer jets and limescale deposits, shortening the appliance’s lifespan.
Not all dishwashers require salt, as some regions have pre-treated water. However, for those needing it, the salt reservoir, usually at the dishwasher’s bottom, requires periodic refilling. Using specialized dishwasher salt, distinct from table salt, ensures optimal performance and prevents clogs.
The amount of salt needed varies, but a rule of thumb is to fill the unit without surpassing the waterline. Regular checks and refills, based on water hardness, contribute to maintaining the dishwasher’s efficiency. Even in areas with naturally soft water, using salt and adjusting water hardness settings is advisable.
Explaining the water-filled salt reservoir dispels concerns, emphasizing its role in creating a salt brine for the softening system. Additionally, the guide touches on rinse aid, clarifying its purpose in preventing watermarks and aiding the drying process. Unlike dishwasher salt, running without rinse aid poses no risk.
Lastly, understanding hard water, characterized by dissolved calcium and magnesium, helps users gauge their water’s quality. Guidelines for water hardness classifications are provided, offering insights into water quality and its impact on daily tasks.
For more detailed information, you can read the full article on dishwasher salt here.


